- Your cart is empty
- Continue Shopping
Types of Fungal Infections, Causes, and Treatments
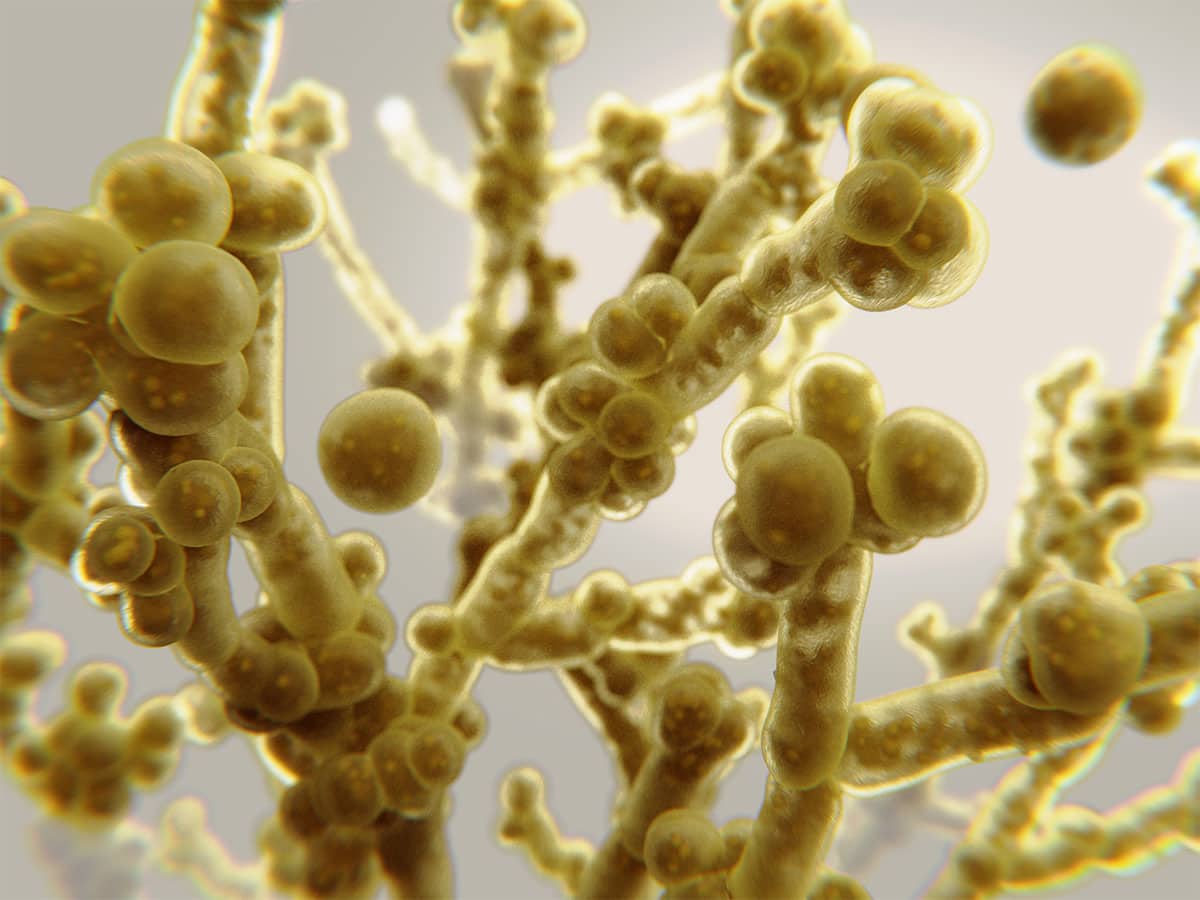
Fungal infections are quite common in all individuals and occur externally on all skin regions of the human body as well as internally within the blood, the lungs, and other organs in the body.
Infections caused by a fungus will often be benign; however, there are cases in which fungal infections can spread and cause extensive illness.
In what follows, we’ll discuss the characteristics of a fungal infection and the signs and symptoms that can be seen. Further, we’ll discuss some different types of fungal infections and their derivatives, including potential treatments and preventative measures that can be utilized.
Characteristics of a Fungal Infection
A fungal infection, also described as mycosis, is the overgrowth of a fungus to the point of causing a significant inflammatory response in the surrounding area. Three areas of the body that are notable for fungal infections are the skin, blood, and lungs. Different fungal types will cause specific infections in these areas in particular circumstances.
The types of fungal infections found in the skin include ringworm, athlete’s foot, jock itch, and other yeast infections. Fungal skin infections are prevalent with the foot being the most common area to find this infection. Fungal skin infections are not life-threatening; however, they can result in moderate symptomatology.
The most common type of fungal infection of the blood is candidemia, otherwise known as invasive candidiasis. Candida is a common skin fungus, and there are various ways in which this fungus can infect the blood. This process can result in severe infection and sepsis, which can lead to the risk of death.
Finally, the types of fungal lung infections include aspergillosis, histoplasmosis, and pneumocystis pneumonia.
Causes and Symptoms of Fungal Infections
Fungal infections can occur due to environmental conditions and can occur by direct contact with a fungus or airborne transmission of a fungus. Differing types of fungi are found in certain environments. A few examples of fungi that can cause infection include candida, Blastomyces, cryptococcus, coccidioides, and Histoplasma.
While anyone can contract a fungal infection, those that are at greatest risk include individuals with decreased immunity secondary to genetics or poor health and individuals who live in some areas of the world where fungi are environmentally prevalent.
Different symptoms occur with different types of fungus. Symptoms of fungal infection can often start as very mild, but then they subsequently worsen. This moderate progression can lead to severe fungal infection if untreated.
In contrast, those with a healthy immune system and a proactive approach towards the rapid identification of symptoms will likely seek help in a more timely manner leading to much better outcomes.
The following are the most common symptoms of fungal skin infections:
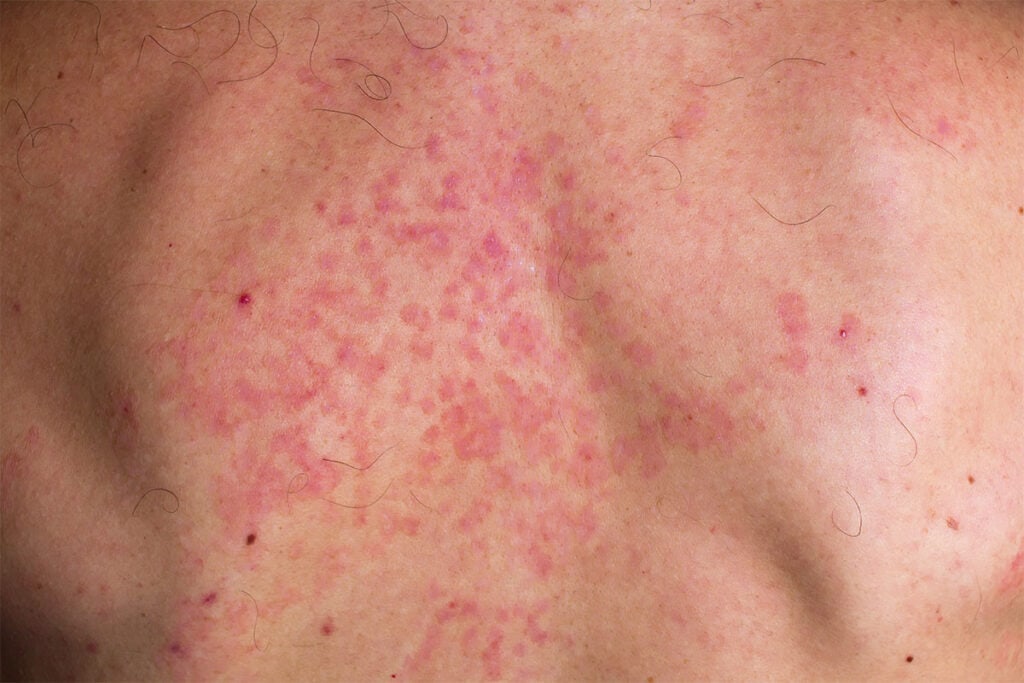
- Swelling of the skin
- Redness of the skin
- Tenderness and itchiness at the source
- Flakes and Growths on the skin
The following are the most common symptoms of fungal lung infections:
- Sore throat
- Persistent and aggressive cough
- Difficulty breathing
- Chest pain
The following are the most common symptoms of fungal blood infections:
- Muscle aches and pains
- High fever and chills
- Low blood pressure
- Extreme weakness and fatigue
- Altered mental status
- Loss of consciousness
These symptoms should prompt an individual to seek medical attention rapidly. Initiation of treatment will lead to the best outcome.
Treatment and Prevention of Fungal Infections
Treating fungal infections will depend on the type and location of the infection. Skin infections, for example, are usually treated with topical antifungal ointments, and sometimes they are treated with oral medications. For fungal infections such as ringworm or athlete’s foot, topical treatment with agents such as miconazole or clotrimazole are very effective. Candida infections of the vaginal mucosa respond well to oral fluconazole. Nail fungal infections are often treated with oral terbinafine.

Fungal infections in the blood and the lungs will require intravenous antifungal medication for treatment. In most recent years, the antifungals called echinocandins have been the most widely used, along with oral antifungal agents such as fluconazole.
The best preventative measure for fungal infection is overall good hygiene. It cannot be expressed how important simple hand washing is in the prevention of infection. Maintaining good nutrition is also imperative in the prevention of fungal infection. Routine skincare of all areas of the body is also preventative. Avoiding unsanitary conditions or taking appropriate precautions when utilizing public facilities is the best way to prevent these infections.
Final Thoughts
Fungal infections are widespread, and most cases can be treated, although the severity of the illness will determine how long treatment will take.
Being aware of the environmental areas where the transmission of fungal illness is high can also help prevent this illness. The most suitable treatment for fungal infections will often be topical antifungals or oral antifungal therapy. It’s important to use the medication for the prescribed length of time to avoid the recurrence of fungal infection.




